Threat Landscape: Malvertising
Malvertising vs. SEO
Malicious advertising, also known as “malvertising,” refers to the use of online advertising to spread malware or to redirect users to malicious websites. Threat actors leveraging malvertising often target various advertisement programs such as Google Adsense, Bing Ads, and Yahoo Gemini. To display the malvertisement, you often must mimic the user search with the same search engine.
These advertisement programs use a Traffic Distribution System (TDS), which is a type of network infrastructure that is used to distribute network traffic across multiple servers. Unfortunately, TDS can be used by bad actors to spread malware or redirect users to malicious websites.
Unfortunately, the owner(s) of the advertising program are often negligent and do not not take action against known malware distributors leveraging their program. These advertisement programs are often deceptive and lie to the user about the true destination.
Example with fake teamviewer ad listing legitimate domain:
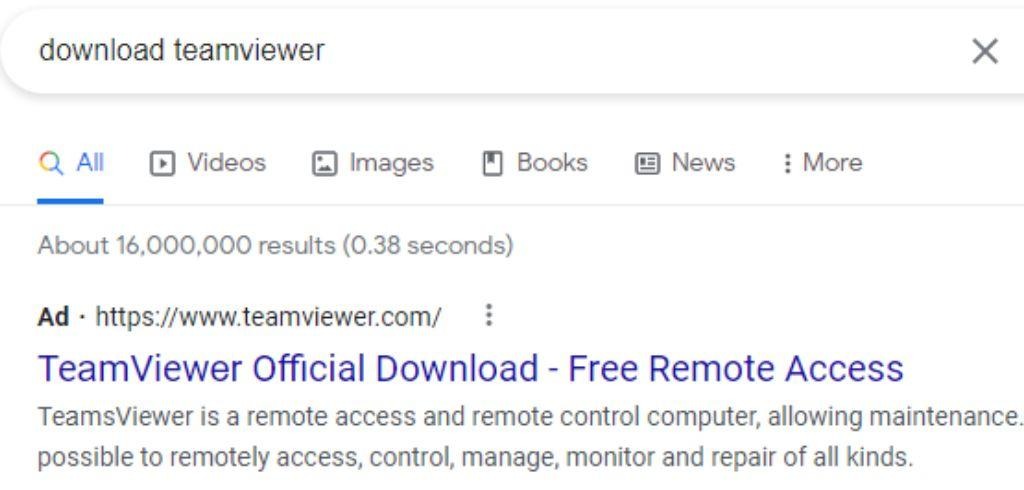
Following the malvertisement campaigns from malware loaders such as Batloader, IcedID, and Redline Stealer throughout mid December of 2022 and early January, the Google Adsense program has been cracking down slightly. Now bad actors cannot lie about the the destination as easily, and proceed to use deceptive naming conventions to mimic the legitimate site.
The malvertising campaigns got enough attention for the FBI to make a PSA with a list of recommendations.
Search engine optimization (SEO), on the other hand, is the practice of improving the visibility of a website in search engine results pages (SERPs). This is done by optimizing the website’s content, structure, and code to make it more attractive to search engines. The goal of SEO is to increase the amount of organic traffic to a website, which can lead to more leads and sales. Unfortunately, a bad actor may use SEO techniques to create fake websites that mimic legitimate businesses, and then use these fake websites to steal personal information from unsuspecting users. For example, a fake online store that looks like a legitimate e-commerce site, but it is instead collecting credit card information from users and using it for fraudulent activities. Malvertising and SEO are often easy to confuse from the analyst perspective.
Abuse with Malvertising
In a period of 12 days, over 400 instances of malvertising has been identified across the industry with different brand targeting.
Mitigations
- Malvertising:
- Use ad-blocking extensions such as #uBlock Origin or run the defaults in browsers such as #LibreWolf or #Brave
- Top Level Domain (TLD) blocking (i.e. [.]top, [.]online)
- Geo-blocking - it is no secret that organizations from Russia/China are responsible for a large amount of malware infections
- Restrict mounting of virtual file systems via GPOs
Not applicable to all malvertising infection chains
- SEO:
- Use a reputable search engine that is less likely to return results from fake websites.
- Check Website authenticity - before entering personal information or making a purchase on a website, make sure the website is legitimate by checking for a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, or checking for customer reviews.
- Anti-phishing software can help protect users from phishing websites by identifying and blocking malicious websites.
- Be aware of suspicious looking websites
- Call to urgency
- Mispellings
- Unprofessional marketing
- General:
- Educate yourself on the common tactics used by bad actors, such as malvertising, SEO, malspam, email thread hijacking, as this can help you identify and avoid these types of attacks.
- Be vigilant when browsing the internet and always be on the lookout for suspicious activity.
References
- Malwarebytes Labs (https://blog.malwarebytes.com/malwarebytes-news/category/malvertising/) - This is a blog dedicated to cybersecurity and specifically covers the topic of malvertising.
- Symantec (https://www.symantec.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/malvertising-definition) - This is a blog run by Symantec, a leading provider of cybersecurity solutions, that covers a range of cybersecurity topics, including malvertising.
- Search Engine Journal (https://www.searchenginejournal.com/seo/) - This is a leading source for SEO news, tips, and best practices.
- Google (https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/35769) - Google provides a range of resources for webmasters, including information on SEO best practices.
These sources can provide you with a range of information to support the information in your post and help you keep up-to-date with the latest developments in the fields of malvertising and SEO.